Introduction
We introduce K-EXAONE, a large-scale multilingual language model developed by LG AI Research. Built using a Mixture-of-Experts architecture, K-EXAONE features 236 billion total parameters, with 23 billion active during inference. Performance evaluations across various benchmarks demonstrate that K-EXAONE excels in reasoning, agentic capabilities, general knowledge, multilingual understanding, and long-context processing.
Key Features
- Architecture & Efficiency: Features a 236B fine-grained MoE design (23B active) optimized with Multi-Token Prediction (MTP), enabling self-speculative decoding that boosts inference throughput by approximately 1.5x.
- Long-Context Capabilities: Natively supports a 256K context window, utilizing a 3:1 hybrid attention scheme with a 128-token sliding window to significantly minimize memory usage during long-document processing.
- Multilingual Support: Covers 6 languages: Korean, English, Spanish, German, Japanese, and Vietnamese. Features a redesigned 150k vocabulary with SuperBPE, improving token efficiency by ~30%.
- Agentic Capabilities: Demonstrates superior tool-use and search capabilities via multi-agent strategies.
- Safety & Ethics: Aligned with universal human values, the model uniquely incorporates Korean cultural and historical contexts to address regional sensitivities often overlooked by other models. It demonstrates high reliability across diverse risk categories.
For more details, please refer to the technical report and GitHub.
Model Configuration
- Number of Parameters: 236B in total and 23B activated
- Number of Parameters (without embeddings): 234B
- Hidden Dimension: 6,144
- Number of Layers: 48 Main layers + 1 MTP layers
- Hybrid Attention Pattern: 12 x (3 Sliding window attention + 1 Global attention)
- Sliding Window Attention
- Number of Attention Heads: 64 Q-heads and 8 KV-heads
- Head Dimension: 128 for both Q/KV
- Sliding Window Size: 128
- Global Attention
- Number of Attention Heads: 64 Q-heads and 8 KV-heads
- Head Dimension: 128 for both Q/KV
- No Rotary Positional Embedding Used (NoPE)
- Mixture of Experts:
- Number of Experts: 128
- Number of Activated Experts: 8
- Number of Shared Experts: 1
- MoE Intermediate Size: 2,048
- Vocab Size: 153,600
- Context Length: 262,144 tokens
- Knowledge Cutoff: Dec 2024 (2024/12)
Evaluation Results
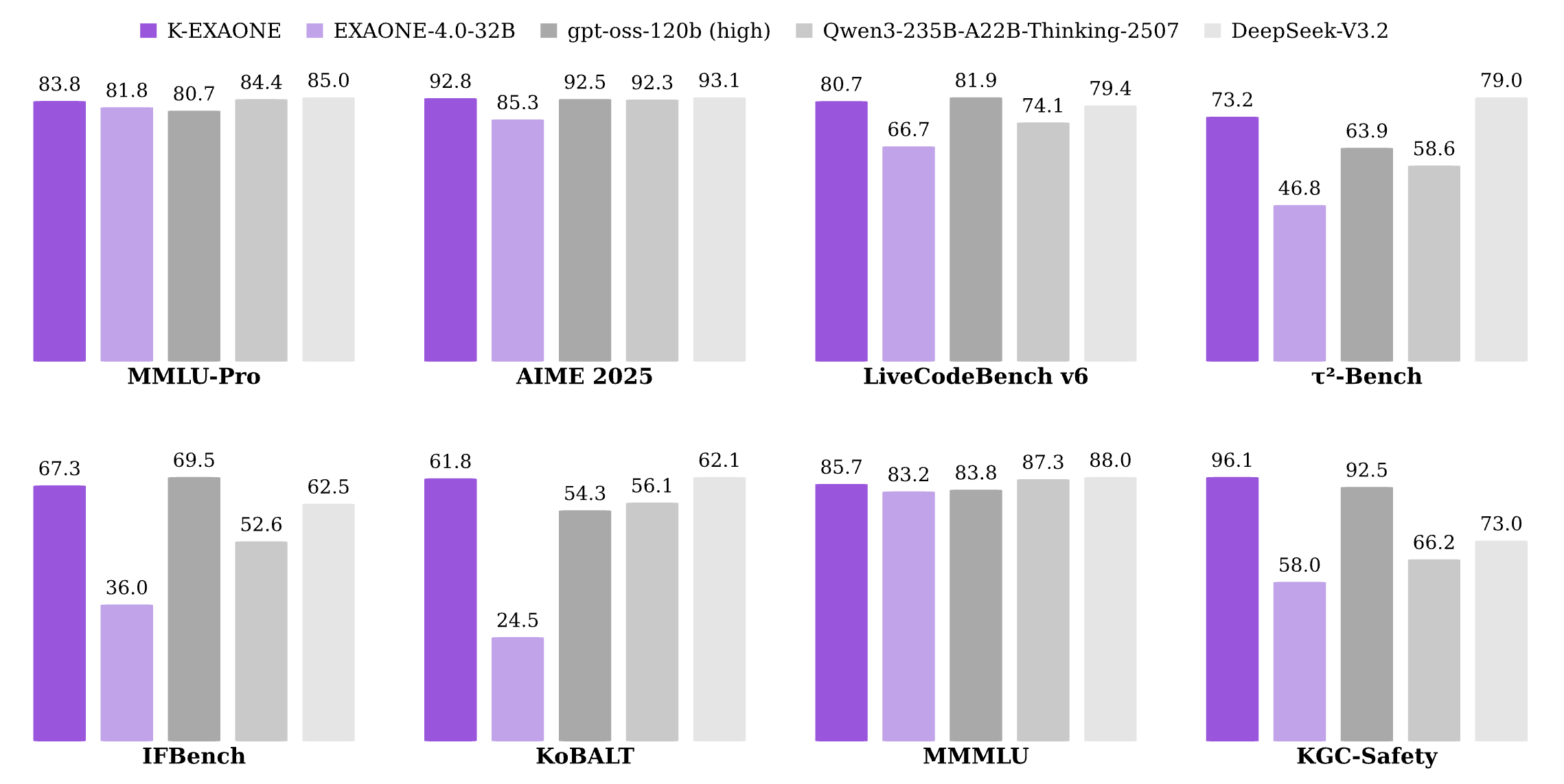
The following table shows the evaluation results of the K-EXAONE model in reasoning mode, compared to our previous model, EXAONE-4.0, and other competing models. The evaluation details can be found in the technical report.
| K-EXAONE (Reasoning) | EXAONE 4.0 (Reasoning) | GPT-OSS (Reasoning: High) | Qwen3-Thinking-2507 | DeepSeek-V3.2 (Reasoning) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Architecture | MoE | Dense | MoE | MoE | MoE | |
| Total Params | 236B | 32B | 117B | 235B | 671B | |
| Active Params | 23B | 32B | 5.1B | 22B | 37B | |
| World Knowledge | ||||||
| MMLU-Pro | 83.8 | 81.8 | 80.7 | 84.4 | 85.0 | |
| GPQA-Diamond | 79.1 | 75.4 | 80.1 | 81.1 | 82.4 | |
| Humanity's Last Exam | 13.6 | 10.6 | 14.9 | 18.2 | 25.1 | |
| Math | ||||||
| IMO-AnswerBench | 76.3 | 66.1 | 75.6 | 74.8 | 78.3 | |
| AIME 2025 | 92.8 | 85.3 | 92.5 | 92.3 | 93.1 | |
| HMMT Nov 2025 | 86.8 | 78.1 | 84.9 | 88.8 | 90.2 | |
| Coding / Agentic Coding | ||||||
| LiveCodeBench Pro 25Q2 (Medium) | 25.9 | 4.8 | 35.4 | 16.0 | 27.9 | |
| LiveCodeBench v6 | 80.7 | 66.7 | 81.9 | 74.1 | 79.4 | |
| Terminal-Bench 2.0 | 29.0 | - | 18.7 | 13.3 | 46.4 | |
| SWE-Bench Verified | 49.4 | - | 62.4 | 25.0 | 73.1 | |
| Agentic Tool Use | ||||||
| τ2-Bench (Retail) | 78.6 | 67.5 | 69.1 | 71.9 | 77.9 | |
| τ2-Bench (Airline) | 60.4 | 52.0 | 60.5 | 58.0 | 66.0 | |
| τ2-Bench (Telecom) | 73.5 | 23.7 | 60.3 | 45.6 | 85.8 | |
| BrowseComp | 31.4 | - | - | - | 51.4 | |
| Instruction Following | ||||||
| IFBench | 67.3 | 36.0 | 69.5 | 52.6 | 62.5 | |
| IFEval | 89.7 | 84.7 | 89.5 | 87.8 | 92.6 | |
| Long Context Understanding | ||||||
| AA-LCR | 53.5 | 14.0 | 50.7 | 67.0 | 65.0 | |
| OpenAI-MRCR | 52.3 | 20.1 | 29.9 | 58.6 | 57.7 | |
| Korean | ||||||
| KMMLU-Pro | 67.3 | 67.7 | 62.4 | 71.6 | 72.1 | |
| KoBALT | 61.8 | 25.4 | 54.3 | 56.1 | 62.7 | |
| CLIcK | 83.9 | 78.8 | 74.6 | 81.3 | 86.3 | |
| HRM8K | 90.9 | 89.4 | 91.6 | 92.0 | 90.6 | |
| Ko-LongBench | 86.8 | 68.0 | 82.2 | 83.2 | 87.9 | |
| Multilinguality | ||||||
| MMMLU | 85.7 | 83.2 | 83.8 | 87.3 | 88.0 | |
| WMT24++ | 90.5 | 80.8 | 93.6 | 94.7 | 90.0 | |
| Safety | ||||||
| Wild-Jailbreak | 89.9 | 62.8 | 98.2 | 85.5 | 79.1 | |
| KGC-Safety | 96.1 | 58.0 | 92.5 | 66.2 | 73.0 | |
Requirements
Until the libraries officially support K-EXAONE, you need to install the requirements in our version with the EXAONE-MoE implementations. We will announce when these libraries are updated to support the K-EXAONE model.
Transformers
You can install the latest version of Transformers with support for EXAONE-MoE architecture from this repository.
The base version of Transformers is 5.0.0rc1, so it might be helpful to check the migration guide from the Transformers library.
vLLM
You should install both Transformers and vLLM to use K-EXAONE model on vLLM server. You can install the latest version of vLLM with support for EXAONE-MoE architecture from this repository.
SGLang
You should install both Transformers and SGLang to use K-EXAONE model on SGLang server. You can install the latest version of SGLang with support for EXAONE-MoE architecture from this repository.
llama.cpp
You can install the latest version of llama.cpp with support for EXAONE-MoE architecture from this repository. Please refer to the official build guide for details.
Quickstart
You can use the K-EXAONE model with the Transformers library. For better quality, you should check the usage guideline section.
Reasoning mode
For tasks that require accurate results, you can run the K-EXAONE model in reasoning mode as below.
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
model_name = "LGAI-EXAONE/K-EXAONE-236B-A23B"
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
dtype="bfloat16",
device_map="auto",
)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are K-EXAONE, a large language model developed by LG AI Research in South Korea, built to serve as a helpful and reliable assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "Which one is bigger, 3.9 vs 3.12?"}
]
input_ids = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=True,
add_generation_prompt=True,
return_tensors="pt",
enable_thinking=True, # skippable (default: True)
)
generated_ids = model.generate(
**input_ids.to(model.device),
max_new_tokens=16384,
temperature=1.0,
top_p=0.95,
)
output_ids = generated_ids[0][input_ids['input_ids'].shape[-1]:]
print(tokenizer.decode(output_ids, skip_special_tokens=True))
Non-reasoning mode
For tasks where latency matters more than accuracy, you can run the K-EXAONE model in non-reasoning mode as below.
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are K-EXAONE, a large language model developed by LG AI Research in South Korea, built to serve as a helpful and reliable assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "Explain how wonderful you are"}
]
input_ids = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=True,
add_generation_prompt=True,
return_tensors="pt",
enable_thinking=False,
)
generated_ids = model.generate(
**input_ids.to(model.device),
max_new_tokens=1024,
temperature=1.0,
top_p=0.95,
)
output_ids = generated_ids[0][input_ids['input_ids'].shape[-1]:]
print(tokenizer.decode(output_ids, skip_special_tokens=True))
Agentic tool use
For your AI-powered agent, you can integrate external functionalities in the following OpenAI-style tool description format. Here is an example of creating a tool description from a Python function.
Please check the example file for an example of a search agent conversation using K-EXAONE.
from transformers.utils import get_json_schema
def roll_dice(max_num: int):
"""
Roll a dice with the number 1 to N. User can select the number N.
Args:
max_num: The maximum number on the dice.
"""
return random.randint(1, max_num)
tool_schema = get_json_schema(roll_dice)
tools = [tool_schema]
messages = [
{"role": "system", "content": "You are K-EXAONE, a large language model developed by LG AI Research in South Korea, built to serve as a helpful and reliable assistant."},
{"role": "user", "content": "Roll a D20 twice and sum the results."}
]
input_ids = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=True,
add_generation_prompt=True,
return_tensors="pt",
tools=tools,
)
generated_ids = model.generate(
**input_ids.to(model.device),
max_new_tokens=16384,
temperature=1.0,
top_p=0.95,
)
output_ids = generated_ids[0][input_ids['input_ids'].shape[-1]:]
print(tokenizer.decode(output_ids, skip_special_tokens=True))
Usage Guideline
To achieve the expected performance, we recommend using the following configurations:
- We strongly recommend to use
temperature=1.0,top_p=0.95,presence_penalty=0.0for best performance.- Different from EXAONE-4.0, K-EXAONE uses
enable_thinking=Trueas default. Thus, you need to setenable_thinking=Falsewhen you want to use non-reasoning mode.
Deployment
TensorRT-LLM
TensorRT-LLM support for the K-EXAONE model is being prepared. Please refer to the EXAONE-MoE PR on TensorRT-LLM repository for details.
vLLM
We support the K-EXAONE model on vLLM. You need to install our fork of the vLLM library to use the K-EXAONE model. Please check the requirements section. Practically, you can serve the model with a 256K context length using tensor parallel on 4 H200 GPUs.
After you install the vLLM library with an EXAONE-MoE implementation, you can run the vLLM server by following command:
vllm serve LGAI-EXAONE/K-EXAONE-236B-A23B \
--reasoning-parser deepseek_v3 \
--enable-auto-tool-choice \
--tool-call-parser hermes
An OpenAI-compatible API server will be available at http://localhost:8000/v1.
You can test the vLLM server by sending a chat completion request as below:
curl -X POST http://localhost:8000/v1/chat/completions \
-H "Content-Type: application/json" \
-d '{
"model": "LGAI-EXAONE/K-EXAONE-236B-A23B",
"messages": [
{"role": "user", "content": "How many r'\''s in \"strawberry\"?"}
],
"max_tokens": 16384,
"temperature": 1.0,
"top_p": 0.95,
"chat_template_kwargs": {"enable_thinking": true}
}'
If you are interested in using MTP weights for speculative decoding, add according options as below.
vllm serve LGAI-EXAONE/K-EXAONE-236B-A23B \
--reasoning-parser deepseek_v3 \
--enable-auto-tool-choice \
--tool-call-parser hermes \
--no-enable-prefix-caching \
--speculative_config '{
"method": "mtp",
"num_speculative_tokens": 2
}'
SGLang
We support the K-EXAONE model on SGLang. You need to install our fork of the SGLang library to use the K-EXAONE model. Please check the requirements section. Practically, you can serve the model with a 256K context length using tensor parallel on 4 H200 GPUs.
python -m sglang.launch_server \
--model LGAI-EXAONE/K-EXAONE-236B-A23B \
--reasoning-parser qwen3
A SGLang server will be available at http://localhost:30000.
Currently, using the OpenAI-compatible server is incompatible with the
transformers>=5.0.0rc0, so you need to use SGLang native API for now. For native API, please refer to the official documentation.Once the issue is resolved, we will update this section accordingly.
You can test the SGLang server by sending a request as below:
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
import requests
model_name = "LGAI-EXAONE/K-EXAONE-236B-A23B"
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
messages = [
{"role": "user", "content": "How many r'\''s in \"strawberry\"?"}
]
input_text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True,
return_tensors="pt",
)
response = requests.post(
f"http://localhost:30000/generate",
json={
"text": input_text,
"sampling_params": {
"temperature": 1.0,
"top_p": 0.95,
"max_new_tokens": 16384,
},
},
)
print(response.json()['text'])
If you are interested in in using MTP weights for speculative decoding, add according options as below.
python -m sglang.launch_server \
--model LGAI-EXAONE/K-EXAONE-236B-A23B \
--reasoning-parser qwen3 \
--speculative-algorithm EAGLE \
--speculative-num-steps 3 \
--speculative-eagle-topk 1 \
--speculative-num-draft-tokens 4
Limitation
The K-EXAONE language model has certain limitations and may occasionally generate inappropriate responses. The language model generates responses based on the output probability of tokens, and it is determined during learning from training data. While we have made every effort to exclude personal, harmful, and biased information from the training data, some problematic content may still be included, potentially leading to undesirable responses. Please note that the text generated by K-EXAONE language model does not reflect the views of LG AI Research.
- Inappropriate answers may be generated, which contain personal, harmful or other inappropriate information.
- Biased responses may be generated, which are associated with age, gender, race, and so on.
- The generated responses rely heavily on statistics from the training data, which can result in the generation of semantically or syntactically incorrect sentences.
- Since the model does not reflect the latest information, the responses may be false or contradictory.
LG AI Research strives to reduce potential risks that may arise from K-EXAONE language models. Users are not allowed to engage in any malicious activities (e.g., keying in illegal information) that may induce the creation of inappropriate outputs violating LG AI's ethical principles when using K-EXAONE language models.
License
The model is licensed under K-EXAONE AI Model License Agreement
Citation
@article{k-exaone,
title={K-EXAONE Technical Report},
author={{LG AI Research}},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:TBD},
year={2025}
}
Contact
LG AI Research Technical Support: [email protected]
- Downloads last month
- 250

-E343BD?style=for-the-badge)